The world of cryptocurrency is constantly evolving, bringing forth innovative tools and methods to enhance user experience and maximize investment potential.
One such revolutionary tool is liquid staking, which allows users to access the value of their staked tokens for other purposes without sacrificing staking rewards.
What is Liquid Staking and How Does it Work?
Liquid staking provides a solution for those seeking the benefits of staking without losing access to their assets.
Unlike traditional staking, which locks up tokens until they are unstaked, liquid staking enables users to retain access to their staked assets’ value.
This flexibility opens up a plethora of opportunities in decentralized finance (DeFi) and other web3 protocols, allowing for more dynamic and strategic asset management.
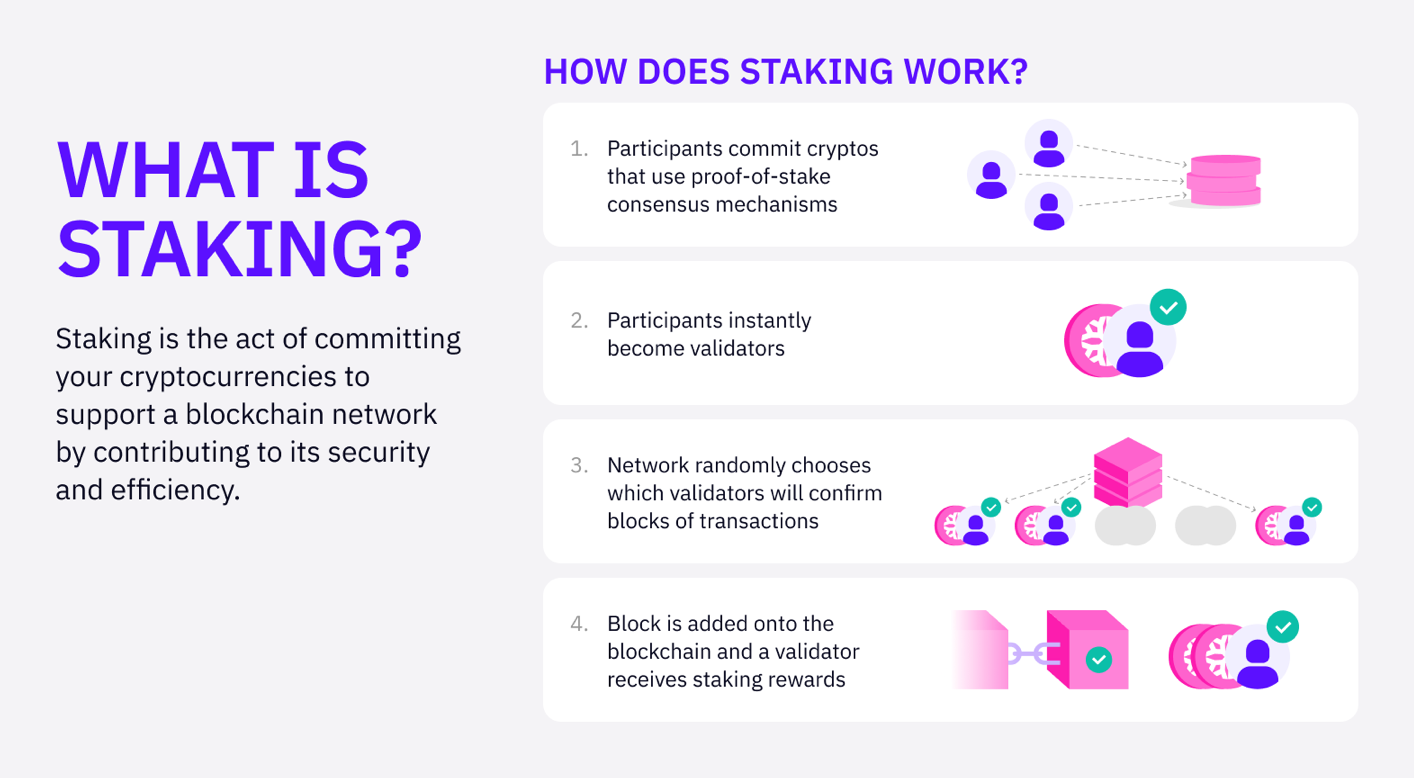
The Basics: Understanding Staking
Before delving into liquid staking, it’s important to grasp the concept of staking itself.
Staking involves validators locking up the native tokens of a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain to earn the chance to validate blocks in the network.
This process not only secures the network but also rewards validators with additional tokens. By staking their tokens, validators are incentivized to act in the best interest of the blockchain, thus maintaining its integrity and security.
Staking is a fundamental mechanism that supports the sustainability and growth of PoS networks.
How Liquid Staking Works
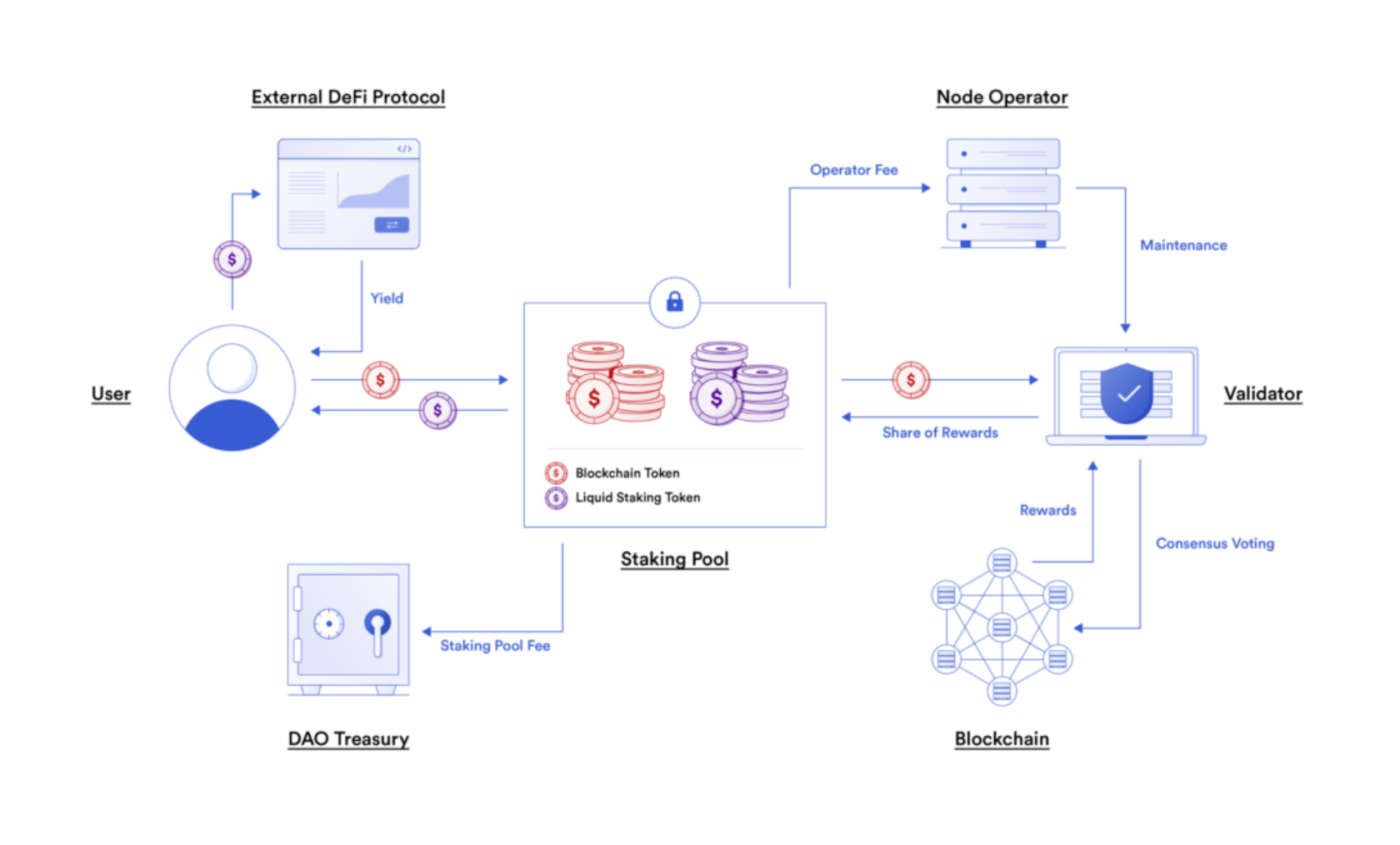
To participate in liquid staking, users lock their cryptocurrency tokens, such as ether, solana or DeFiChain, in a smart contract or platform that supports staking.
In return, they receive staking rewards and a liquid staking token (LST), representing the staked asset.
These LSTs can be traded or used as collateral in various DeFi platforms, unlocking the inherent value of the staked tokens.
This system enables users to benefit from staking rewards while simultaneously leveraging their assets for other financial activities, enhancing their overall liquidity and investment potential.
Restaking and Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRTs)
Restaking allows users to further enhance their earnings by “restaking” their staked assets and LSTs in third-party protocols for additional rewards.
Specialized restaking protocols issue liquid restaking tokens (LRTs), which represent ownership of the underlying restaked assets, adding another layer of potential income.
This multi-tiered approach to staking and restaking creates a robust ecosystem for maximizing returns and utilizing staked assets across multiple platforms.
Benefits of Liquid Staking
- Unlocked Liquidity: Traditional staking locks tokens, preventing them from being traded or used as collateral. Liquid staking tokens unlock this value, enabling their use across various DeFi protocols. This access to liquidity allows investors to participate more actively in the market without sacrificing their staking rewards.
- Composability in DeFi: Liquid staking tokens can be utilized in a wide array of DeFi applications, such as lending pools and prediction markets, enhancing the overall utility of staked assets. This composability fosters greater innovation and integration within the DeFi ecosystem.
- Reward Opportunities: Users continue to earn staking rewards while also generating additional yield through DeFi protocols, maximizing their investment returns. This dual earning potential makes liquid staking an attractive option for both novice and experienced investors.
- Outsourced Infrastructure Requirements: Liquid staking providers manage the complex staking infrastructure, allowing users to share in staking rewards without needing the minimum tokens required to be a solo validator. This democratizes access to staking, enabling more users to participate and benefit from blockchain networks.
Risks and Limitations of Liquid Staking
- Slashing: Relying on a liquid staking provider means users are exposed to the risk of their funds being slashed if the provider acts maliciously or unreliably. Ensuring the trustworthiness and reliability of the staking provider is crucial to mitigate this risk.
- Exploits: Funds are at risk if a node operator’s private keys are compromised or if there are vulnerabilities in the protocol’s smart contracts. Security audits and robust protocols are essential to safeguard against such exploits.
- Secondary Market Volatility: The price of liquid staking tokens can fluctuate and may drop below the value of the underlying asset during liquidity crunches or unexpected events. Market participants must be aware of these volatility risks and prepare accordingly.
Final Thoughts
Liquid staking is a groundbreaking development in the cryptocurrency space, offering increased flexibility and enhanced earning opportunities for stakers.
While it presents significant benefits, including unlocked liquidity, composability in DeFi, and additional reward opportunities, it also comes with risks such as slashing, exploits, and market volatility.
As with any investment strategy, it’s crucial to conduct thorough research and understand the associated risks before participating in liquid staking.



